In recent years, Vietnam has emerged as a hotspot for foreign investment, with its telecommunications sector standing out as a particularly attractive opportunity. This comprehensive guide explores the landscape of foreign investment in Vietnam’s telecommunications industry, providing valuable insights for potential investors and industry stakeholders.
1. Introduction
Vietnam’s telecommunications sector has experienced rapid growth and transformation over the past decade. With a population of over 97 million and a growing middle class, the country presents a lucrative market for telecom services. The Vietnamese government has recognized the importance of foreign investment in driving innovation and competition in this critical sector.
Brief overview of Vietnam’s telecom sector
The Vietnamese telecom market is characterized by high mobile penetration rates, increasing internet usage, and a shift towards advanced technologies like 4G and 5G networks. Major players in the market include both state-owned enterprises and private companies, creating a dynamic and competitive environment.
Importance of foreign investment in the industry
Foreign investment plays a crucial role in Vietnam’s telecom sector by bringing in capital, expertise, and advanced technologies. It contributes to the modernization of infrastructure, improvement of service quality, and overall economic growth of the country.
2. Current State of Vietnam’s Telecommunications Sector
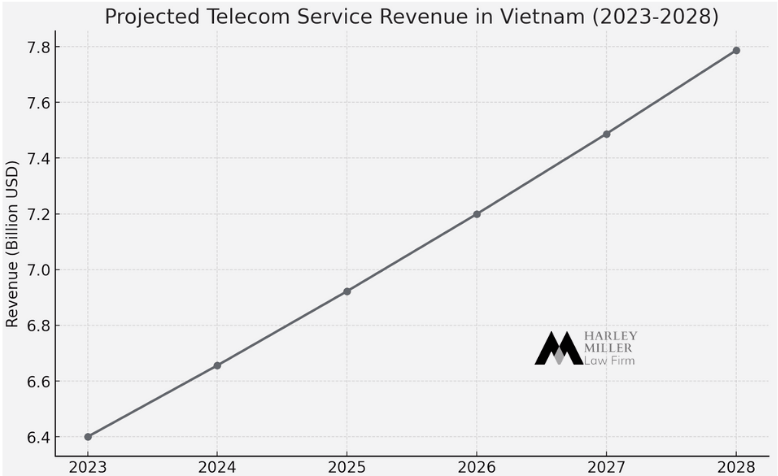
Market size and growth projections
According to recent reports, The total telecom service revenue in Vietnam reached $6.4 billion in 2023. The market size growth has been estimated to incline at a CAGR of more than 4% during 2023-2028. This growth is driven by increasing smartphone adoption, rising internet penetration, and the government’s digital transformation initiatives.
Key players and market share
The Vietnamese telecom market is dominated by three major players:
According to a report on Vietnam’s telecommunications sector, Viettel holds the largest market share at around 50%, followed by VNPT with approximately 25%, and MobiFone with about 20% of the market. The entry of foreign companies through joint ventures and partnerships has further heightened competition and improved service quality in the market (source: VietnamCredit)
Foreign companies have also entered the market through joint ventures and partnerships, contributing to increased competition and service quality.
Recent developments and trends
Key trends shaping the Vietnamese telecom sector include:
- The rapid adoption of 4G and preparation for 5G networks
- Increasing demand for data services and digital content
- Growth in e-commerce and digital payment solutions
- Expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) applications
3. Foreign Investment Opportunities
Areas open for foreign investment
Foreign investors can explore opportunities in various segments of Vietnam’s telecom sector, including:
- Network infrastructure development
- Value-added services and digital content
- Cloud computing and data centers
- Cybersecurity solutions
- IoT and smart city technologies
Success stories of foreign investors
Several foreign companies have successfully entered Vietnam’s telecom market. For example, South Korea’s SK Telecom has partnered with Vingroup to develop and deploy 5G networks in Vietnam. Similarly, Norway’s Telenor Group has invested in digital services and mobile financial solutions in the country.
Potential returns on investment
The Vietnamese telecom sector offers attractive returns for foreign investors. With the country’s strong economic growth, increasing digital adoption, and supportive government policies, investors can expect long-term growth and profitability in this dynamic market.
4. Regulatory Framework for Foreign Investment
Foreign ownership limits and restrictions
While Vietnam has gradually liberalized its telecom sector, some restrictions on foreign ownership remain (according to the WTO Commitment):
- Non-infrastructure services: Allows joint ventures and freedom to choose partners, with the foreign party’s capital contribution capped at 65% of the joint venture’s legal capital.
- Infrastructure-based services: Allows joint ventures with licensed telecommunications service providers in Vietnam. The foreign party’s capital contribution in the joint venture is capped at 49% of the joint venture’s legal capital.
- 51% control: This level of ownership grants control over joint venture management.
Licensing requirements and procedures
Foreign investors must obtain necessary licenses and approvals from the Ministry of Information and Communications (MIC) and other relevant authorities. The licensing process typically involves submitting a detailed business plan, demonstrating financial capacity, and meeting technical requirements.
Recent policy changes affecting foreign investors
The Vietnamese government has introduced several policies to attract foreign investment in the telecom sector, including:
- Streamlining licensing procedures
- Offering tax incentives for high-tech investments
- Encouraging public-private partnerships in infrastructure development
5. Challenges and Considerations
Competition from state-owned enterprises
Foreign investors may face challenges competing with well-established state-owned enterprises that have significant market share and government support. Building strong partnerships and offering innovative services can help overcome this challenge.
Technological infrastructure challenges
While Vietnam has made significant progress in developing its telecom infrastructure, some areas still require substantial investment. Foreign investors should be prepared to contribute to infrastructure development as part of their market entry strategy.
Cultural and business practice differences
Understanding local business culture and practices is crucial for success in Vietnam. Foreign investors should invest time in building relationships with local partners and stakeholders to navigate the market effectively.
6. Future Outlook
5G network development and opportunities
Vietnam aims to become one of the early adopters of 5G technology in Southeast Asia. This presents significant opportunities for foreign investors in areas such as network equipment, software solutions, and 5G-enabled applications.
Emerging technologies and their impact
The integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and edge computing in telecom services is expected to create new investment opportunities and drive innovation in the sector.
Predicted trends in foreign investment
As Vietnam continues to liberalize its telecom sector and improve its business environment, foreign investment is expected to increase. Areas likely to attract significant investment include digital infrastructure, cloud services, and smart city solutions.
7. Conclusion
Vietnam’s telecommunications sector offers compelling opportunities for foreign investors, backed by a growing economy, supportive government policies, and increasing digital adoption. While challenges exist, the potential for growth and innovation in this dynamic market makes it an attractive destination for telecom investments.
As Vietnam continues its journey towards becoming a leading digital economy in Southeast Asia, foreign investors have a unique opportunity to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the country’s telecommunications landscape.
To stay updated on the latest developments and opportunities in Vietnam’s telecommunications sector, subscribe to our newsletter. For personalized advice on investing in Vietnam’s telecom market, don’t hesitate to contact a local investment consultant who can provide tailored guidance based on your specific interests and goals.
Address: 14th floor, HM Town Building, 412 Nguyen Thi Minh Khai, Ward 05, District 3, Ho Chi Minh City.
Phone: +84 937215585
Website: hmlf.vn
Email: miller@hmlf.vn


